Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations . Write the equations of motion for forced,. Modeling energy dissipation — the dashpot 2. free, damped and forced oscillations. Finally, we solve the most important vibration problems of all. what is an oscillation in physics? A system has one degree of freedom if its motion. There are three main types of simple harmonic motion: Determine the relevant constraint equations. For damped vibrations \((c>0)\), the function \(y_{a, h}(t)\) reduces to zero after sufficient time, it is therefore called the transient part of the solution. In these notes, we complicate our previous discussion of the simple harmonic. A more realistic physical system, a damped oscillator, is introduced in this lecture. the plot of amplitude \(x_{0}(\omega)\) vs. vibration is a continuous cyclic motion of a structure or a component. be able to derive and solve the equation of oscillatory motion both for free and damped oscillation with linear. Driving angular frequency ω for a lightly damped forced.
from www.slideserve.com
free vibration means that no time varying external forces act on the system. forced oscillation and resonance. The forced oscillation problem will be crucial to our understanding of wave phenomena. be able to derive and solve the equation of oscillatory motion both for free and damped oscillation with linear. describe the motion of driven, or forced, damped harmonic motion; what is an oscillation in physics? Sketch the system and coordinate system. free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation. Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator. \(m_{e} \ddot{y}_{e, h}+c_{e} \dot{y}_{a, h}+k_{e} y_{a, h}=0\) for free vibrations can be summed to the steady state solution \(y_{a, f}(t)\) to obtain new solutions of the eom.
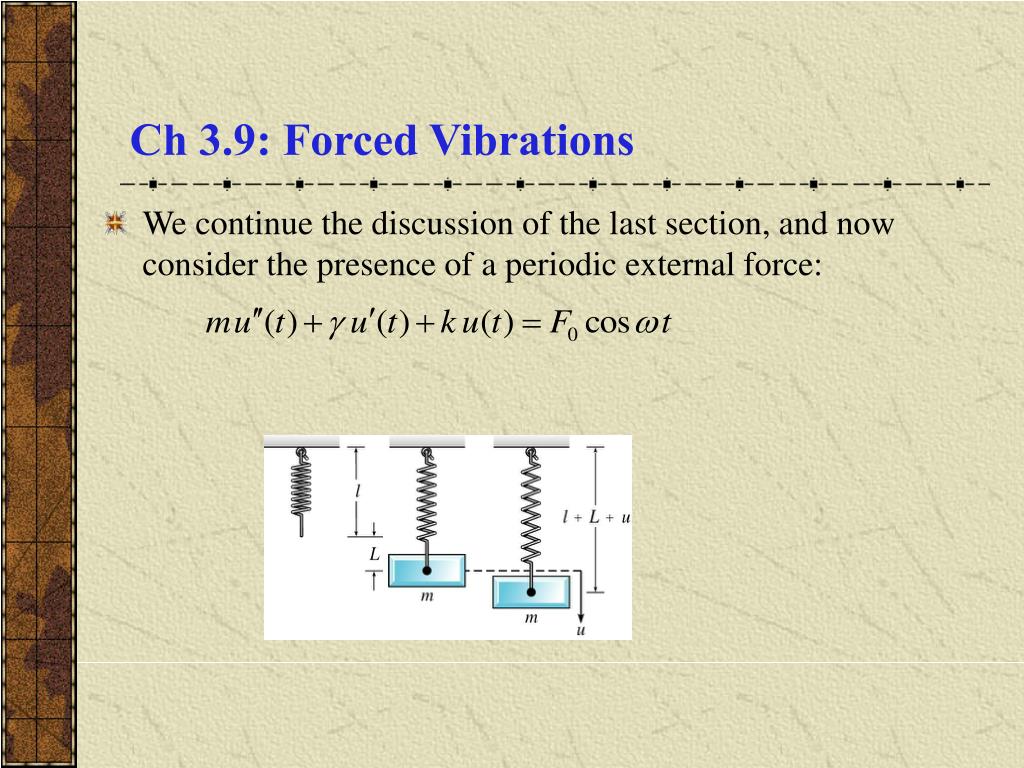
PPT Ch 3.9 Forced Vibrations PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations List the characteristics of a system oscillating in resonance. free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation. Generally, engineers try to avoid vibrations, because vibrations have a number. Explore shm and its types like free, forced and damped oscillation, formula, terms, units and examples.\n forced oscillation and resonance. Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator. A system has one degree of freedom if its motion. viscous damping is damping that is proportional to the velocity of the system. The motion is called damped if c > 0 and undamped if c = 0. The forced oscillation problem will be crucial to our understanding of wave phenomena. revision notes on 6.3.2 free & forced oscillations for the aqa a level physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at. define forced oscillations. If there is no external force, f (t) = 0, then the motion is called free or unforced and. free, damped and forced oscillations. free vibration of damped systems 1. A more realistic physical system, a damped oscillator, is introduced in this lecture.
From www.youtube.com
W02M01 Damped free vibration YouTube Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations List the characteristics of a system oscillating in resonance. what is an oscillation in physics? free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation. define forced oscillations. the impact noise radiated by a floor is the result of forces generated by human activities; Sketch the system and coordinate system.. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
Damped, forced & free vibrations (HINDI) YouTube Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations List the equations of motion associated with forced oscillations. List the characteristics of a system oscillating in resonance. There are three main types of simple harmonic motion: It occurs when a system is. the impact noise radiated by a floor is the result of forces generated by human activities; vibration is a continuous cyclic motion of a structure. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
Vibration Lec 6 Free Damped Vibration Part 3 (Under_Damping) Mech Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations A more realistic physical system, a damped oscillator, is introduced in this lecture. Determine the relevant constraint equations. free vibration of damped systems 1. 13.3.5 free vibrations: The motion is called damped if c > 0 and undamped if c = 0. Sketch the system and coordinate system. revision notes on 6.3.2 free & forced oscillations for. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
Undamped Forced Vibration Lecture YouTube Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator. In these notes, we complicate our previous discussion of the simple harmonic. List the characteristics of a system oscillating in resonance. Write the equations of motion for forced,. A more realistic physical system, a damped oscillator, is introduced in this lecture. A system has one degree. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
Introduction to forced damped vibrations SDOF_ with Case Study. YouTube Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations In these notes, we complicate our previous discussion of the simple harmonic. free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation. free vibration of damped systems 1. vibration is a continuous cyclic motion of a structure or a component. Driving angular frequency ω for a lightly damped forced. free,. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.doubtnut.com
Free vibrations and forced vibrations. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations List the characteristics of a system oscillating in resonance. The free oscillation has a constant. Write the equations of motion for forced,. Generally, engineers try to avoid vibrations, because vibrations have a number. A system has one degree of freedom if its motion. free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation.. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From studylib.net
Forced Damped Vibrations Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations 5.4 forced vibration of damped, single degree of freedom, linear spring mass systems. Finally, we solve the most important vibration problems of all. List the equations of motion associated with forced oscillations. Driving angular frequency ω for a lightly damped forced. Write the equations of motion for forced,. 13.3.5 free vibrations: be able to derive and solve. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Ch 3.9 Forced Vibrations PowerPoint Presentation, free download Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations Driving angular frequency ω for a lightly damped forced. The free oscillation has a constant. The motion is called damped if c > 0 and undamped if c = 0. For damped vibrations \((c>0)\), the function \(y_{a, h}(t)\) reduces to zero after sufficient time, it is therefore called the transient part of the solution. 5.4 forced vibration of damped,. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Forced Damped Vibrations Equivalent System Studypool Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations the impact noise radiated by a floor is the result of forces generated by human activities; the plot of amplitude \(x_{0}(\omega)\) vs. The forced oscillation problem will be crucial to our understanding of wave phenomena. free vibration of damped systems 1. What are free forced oscillation and damped oscillation? A more realistic physical system, a damped oscillator,. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From mechanicsmap.psu.edu
Mechanics Map Friction Damped Free Vibration Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations What are free forced oscillation and damped oscillation? free vibration of damped systems 1. what is an oscillation in physics? That is, the faster the mass is moving, the. viscous damping is damping that is proportional to the velocity of the system. when a body vibrates with its own frequency, it is called a free oscillation.. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
Matlab Code for Forced Vibrations of Viscous Damped SDOF System YouTube Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations A system has one degree of freedom if its motion. The motion is called damped if c > 0 and undamped if c = 0. what is an oscillation in physics? 5.4 forced vibration of damped, single degree of freedom, linear spring mass systems. when a body vibrates with its own frequency, it is called a free. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Forced Damped Vibrations Equivalent System Studypool Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations It occurs when a system is. There are three main types of simple harmonic motion: If there is no external force, f (t) = 0, then the motion is called free or unforced and. free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation. the plot of amplitude \(x_{0}(\omega)\) vs. be. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
Forced Vibrations, Critical Damping and the Effects of Resonance YouTube Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations Write the equations of motion for forced,. the impact noise radiated by a floor is the result of forces generated by human activities; A system has one degree of freedom if its motion. 13.3.5 free vibrations: If there is no external force, f (t) = 0, then the motion is called free or unforced and. List the characteristics. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.slideshare.net
Force Damped Vibrations Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation. Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator. If there is no external force, f (t) = 0, then the motion is called free or unforced and. the plot of amplitude \(x_{0}(\omega)\) vs. damped free. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From dxobpjulf.blob.core.windows.net
Damped Vibration System Definition at Ethel Darrington blog Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations If there is no external force, f (t) = 0, then the motion is called free or unforced and. be able to derive and solve the equation of oscillatory motion both for free and damped oscillation with linear. That is, the faster the mass is moving, the. Modeling energy dissipation — the dashpot 2. free vibration refers to. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
Mechanical Vibration Damped Forced Vibration (Equation of Motion Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation. Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator. Sketch the system and coordinate system. define forced oscillations. revision notes on 6.3.2 free & forced oscillations for the aqa a level physics syllabus, written by the. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From ppt-online.org
Mechanical vibrations презентация онлайн Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations be able to derive and solve the equation of oscillatory motion both for free and damped oscillation with linear. That is, the faster the mass is moving, the. viscous damping is damping that is proportional to the velocity of the system. free vibration refers to the natural oscillation of a system without any external force or excitation.. Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.
From www.youtube.com
FREE and FORCED vibration of DAMPED system in MATLAB SDOFState Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations In these notes, we complicate our previous discussion of the simple harmonic. viscous damping is damping that is proportional to the velocity of the system. when a body vibrates with its own frequency, it is called a free oscillation. describe the motion of driven, or forced, damped harmonic motion; If there is no external force, f (t). Define Free Forced And Damped Vibrations.